About Trend
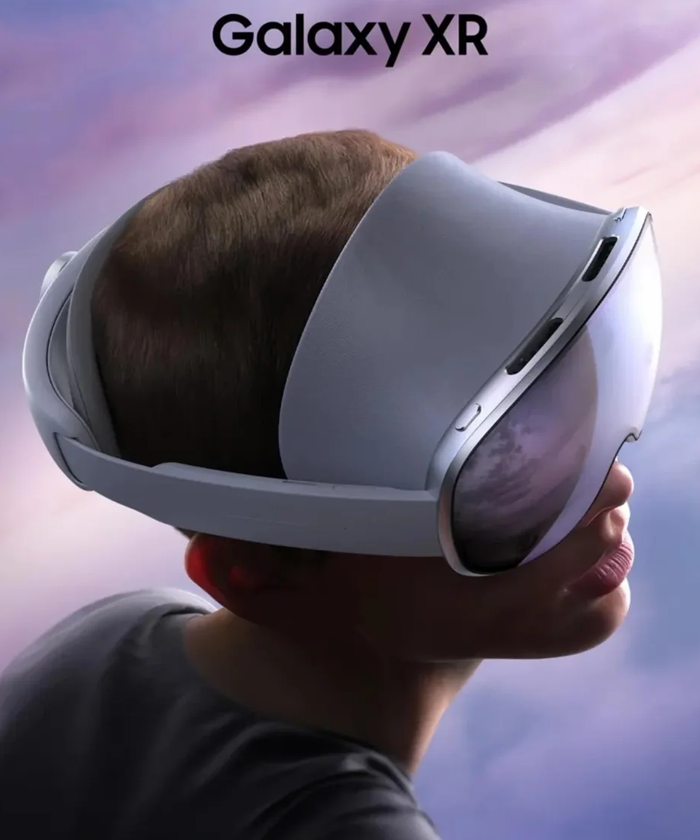
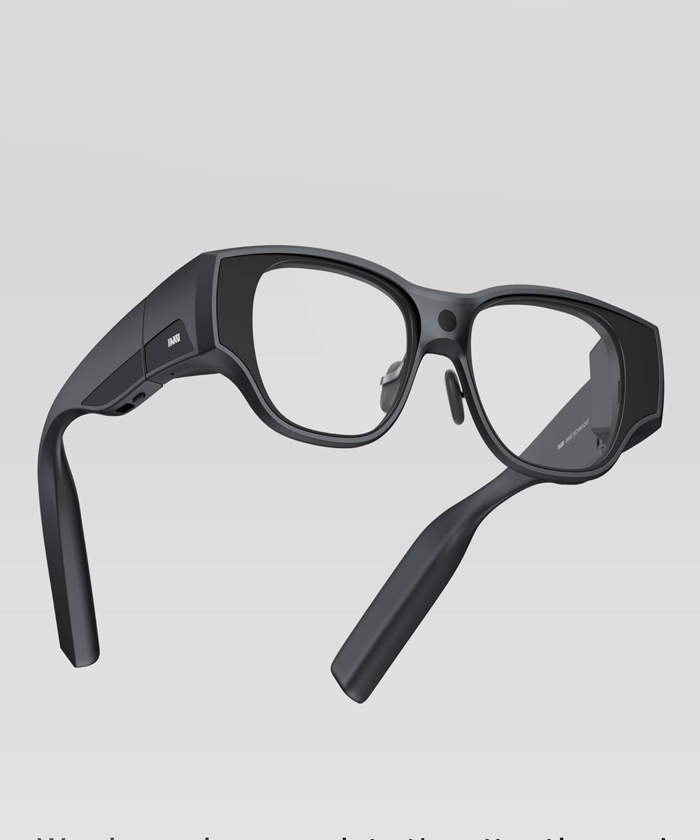
EExtended Reality (XR) headsets and smart glasses have accelerated in popularity throughout 2024 and 2025, evolving from specialised gaming devices into powerful spatial-computing platforms. New generations of hardware—such as the Apple Vision Pro, Meta Quest 3, Pico 4, Samsung Galaxy XR, Vivo Vision, and the latest HTC Vive models—offer more comfortable form factors, sharper optics, and advanced mixed-reality features that blend virtual content naturally with the physical world. In the landscape of smart XR glasses, the technology remains more experimental, but in the coming years, some models are likely to gain wider popularity. Notable examples include INMO, InAir, Rokid, VITURE, and, of course, Meta glasses.
At the same time, AI has become deeply integrated into these devices, powering hand-tracking, eye-tracking, scene understanding, object recognition, personalised interfaces, real-time spatial mapping, and even on-device generative content. This shift makes XR experiences more intuitive, adaptive, and personalised than ever before.
With major tech companies competing to define the future of spatial computing, XR is becoming more accessible and more useful across education, design, retail, training, healthcare, and immersive content creation. As hardware and AI continue to converge, XR is steadily reshaping how people work, learn, and interact with digital information in both virtual and physical environments.

Type of devices
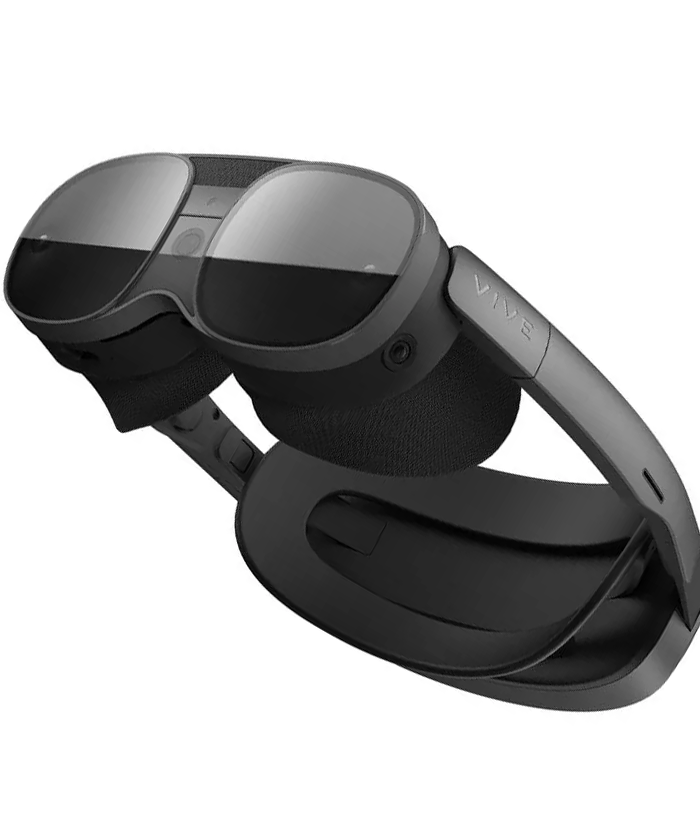
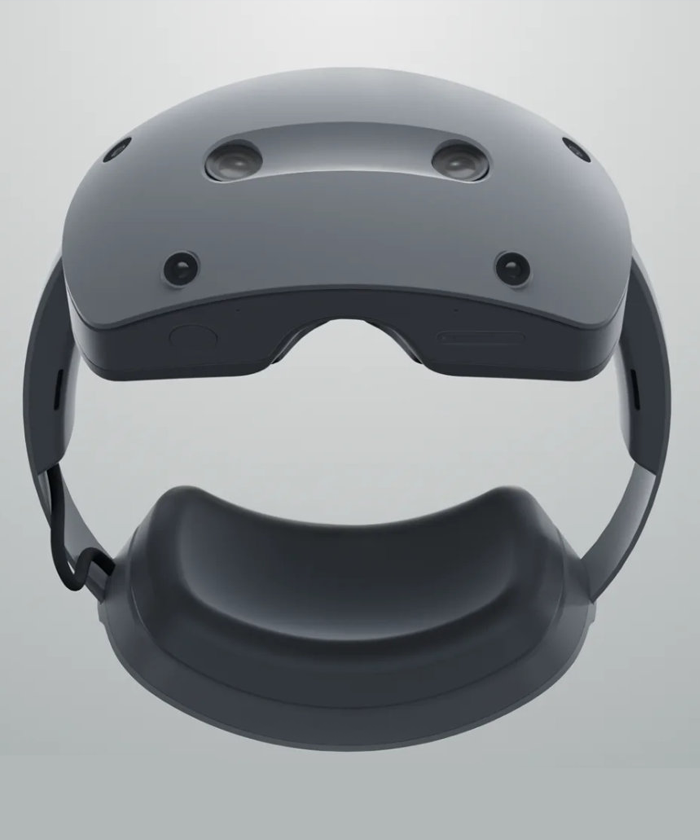
1. XR Headsets
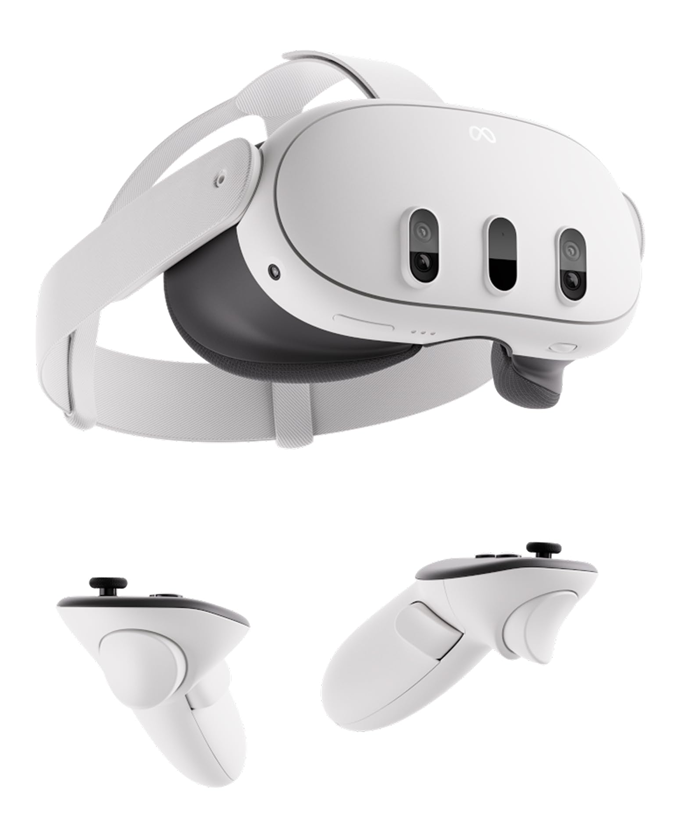
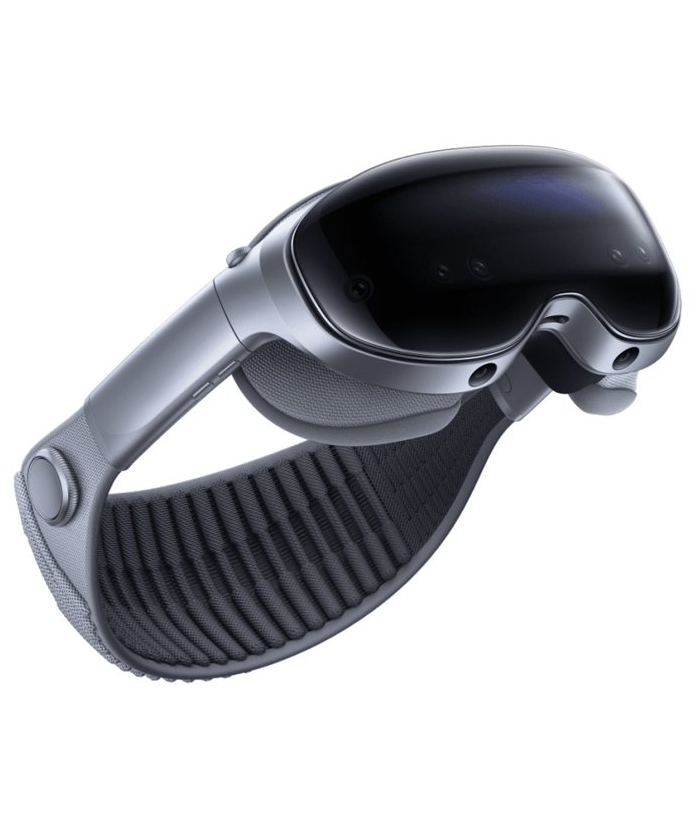
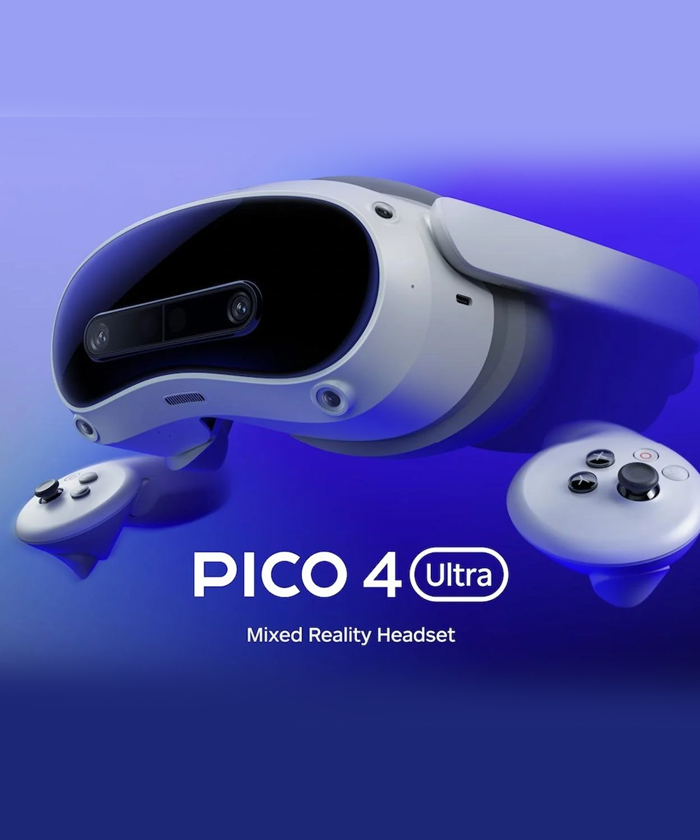
XR headsets are fully immersive devices designed for virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR). They typically include enclosed 4K displays, advanced sensors, inside-out tracking, spatial audio, and powerful onboard processors. These devices—such as the Apple Vision Pro, Meta Quest 3, HTC Vive XR Elite, and Pico 4—are used for gaming, training, productivity, design, education, and enterprise simulations. Because they offer the most advanced capabilities, they deliver deeply immersive spatial experiences but remain bulkier than glasses-style wearables.
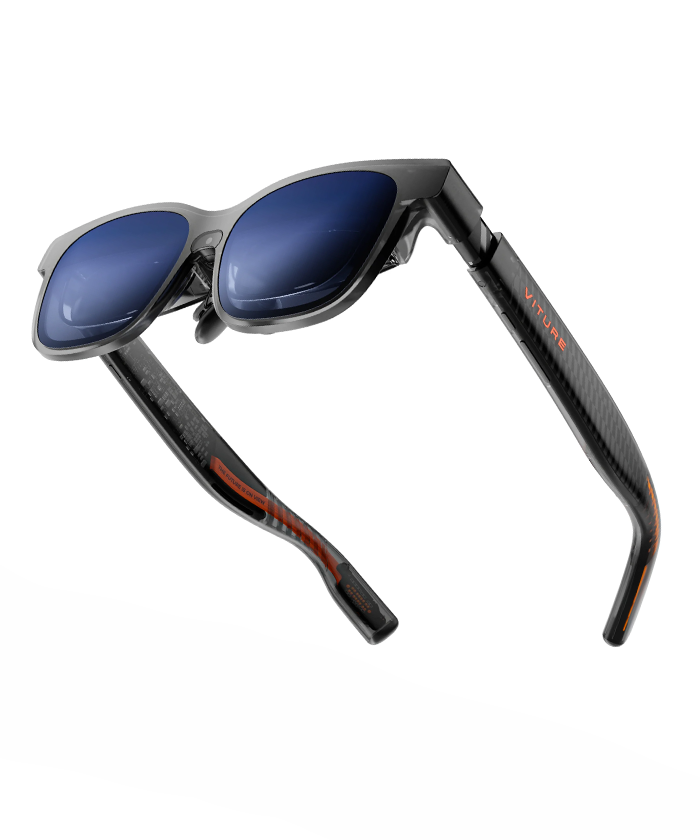
2. XR Glasses (Wired)
Wired XR glasses are lightweight wearable displays that connect to a smartphone, PC, or console via USB-C. The external device provides all the processing power, allowing the glasses to remain thin and comfortable. Examples include the XREAL Air, VITURE XR Glasses, and Samsung’s wired prototypes. These glasses offer high-resolution virtual screens, basic AR overlays, and media consumption, making them ideal for mobility, productivity, and entertainment—without the complexity of a full headset.
3. XR Glasses (Wireless)
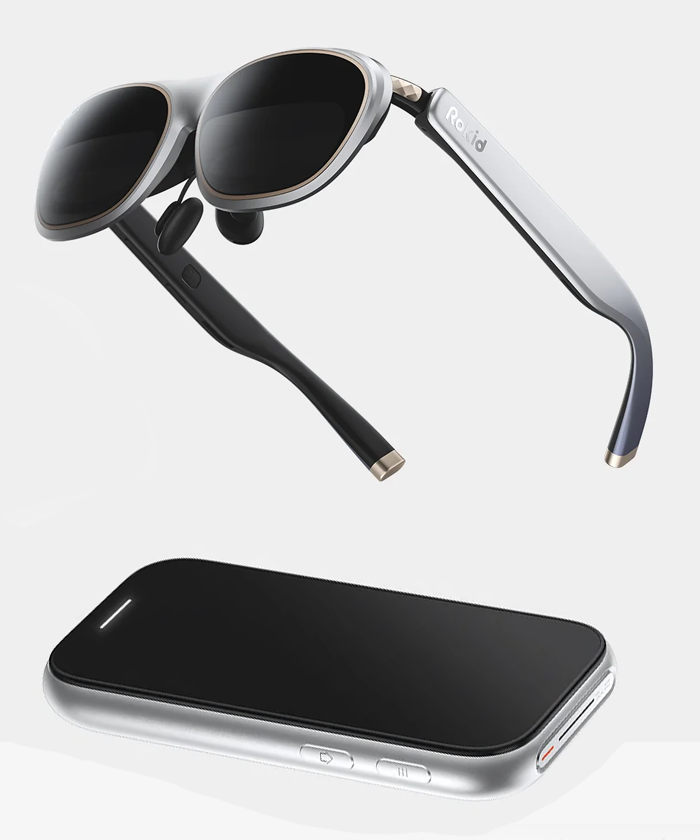
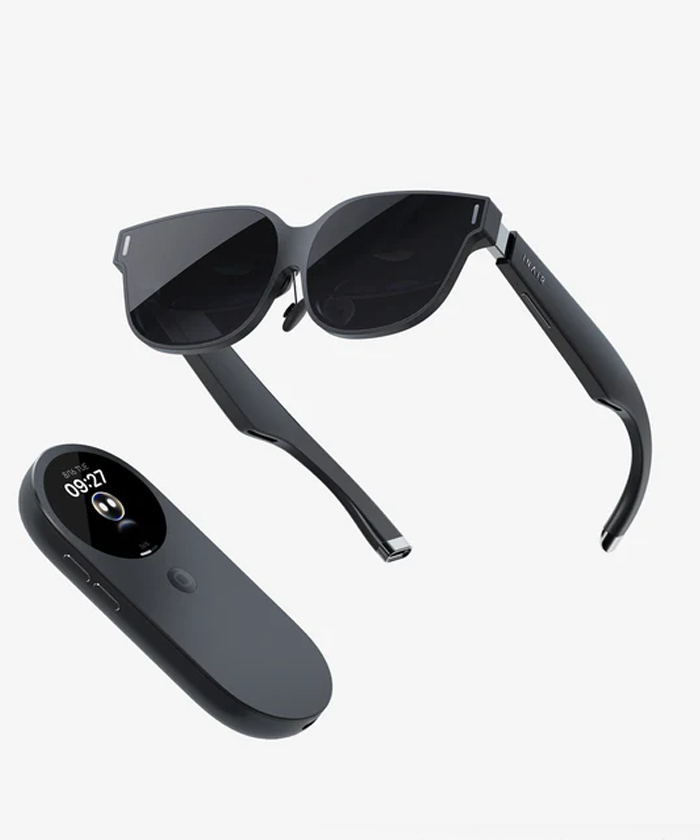
Wireless XR glasses remove the cable and integrate onboard compute, sensors, and batteries. They are still slimmer than headsets but capable of real-time spatial mapping, 6DoF tracking, and interactive AR. Devices in this category—such as the Rokid Max Pro, Vuzix AR glasses, Imno Air3, and emerging wireless XR prototypes—enable hands-free experiences for navigation, remote assistance, lightweight gaming, and mixed-reality tasks. Their portability makes them more social and everyday-friendly than full XR headsets.
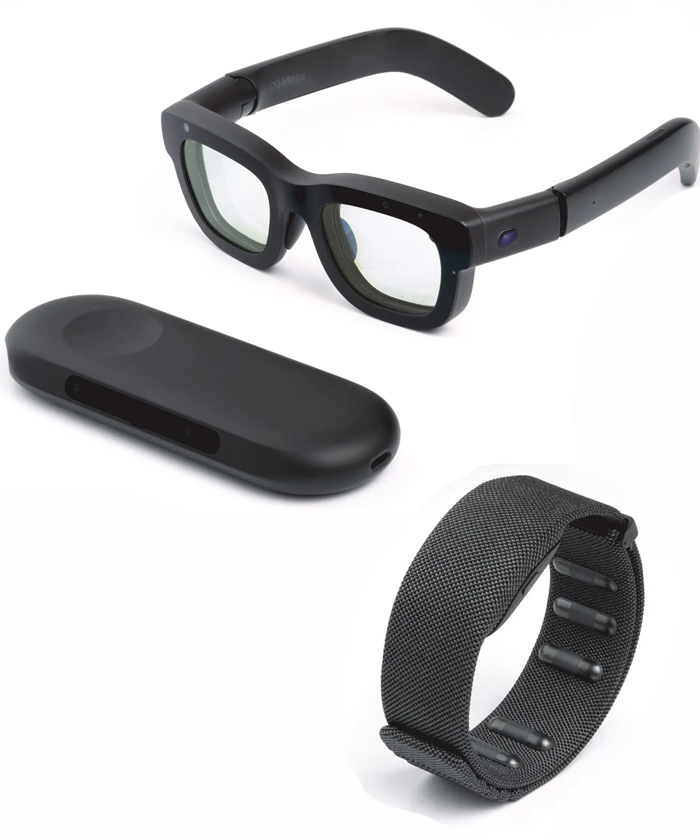
4. AI Glasses
AI glasses represent a new category focused on AI assistance rather than immersive spatial visuals. These glasses typically feature microphones, cameras, speakers, and small displays, integrating conversational AI, real-time translation, contextual assistance, and object recognition. Examples include Meta Ray-Ban Smart Glasses and other early AI-wearables emerging in 2025. They are designed for seamless daily use, offering hands-free information, multimedia capture, and AI-driven personal assistance rather than full mixed reality.